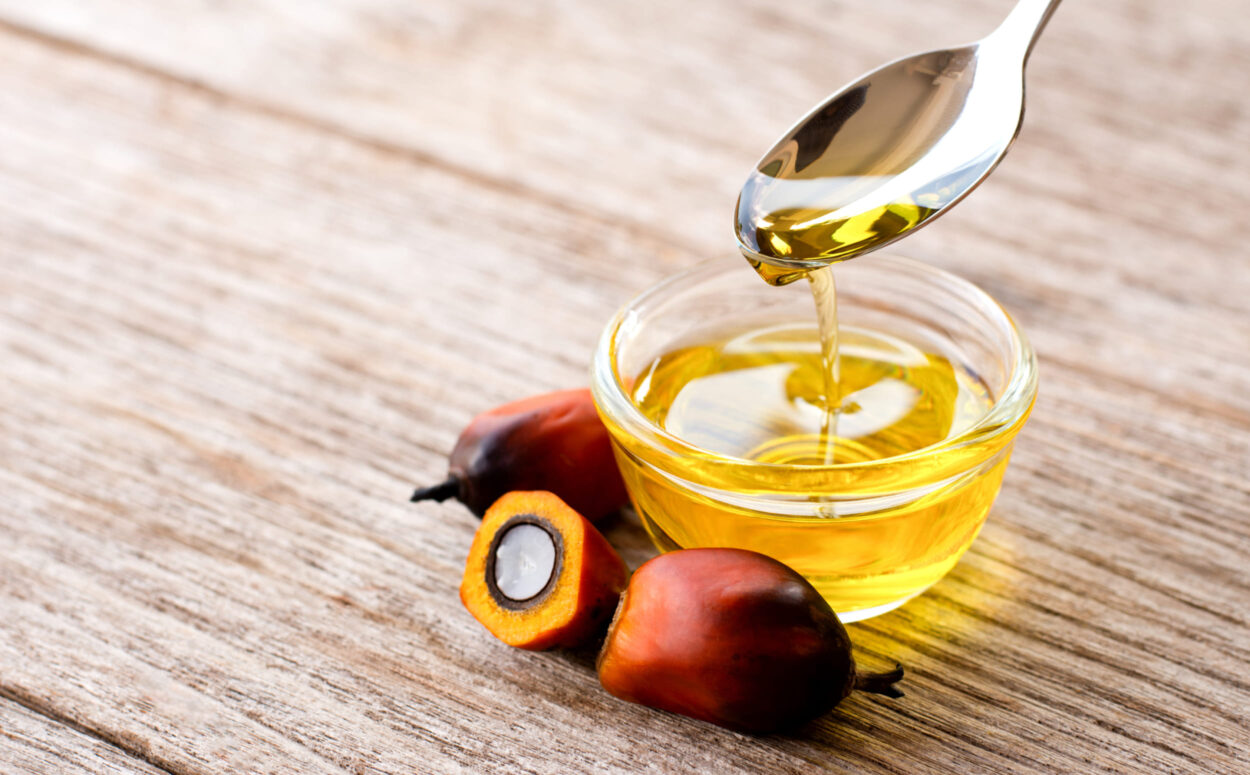
Is palm oil good for you or bad for you?
While concerns have arisen about whether palm oil is harmful for health, it’s important to understand that like any dietary component, moderation is key.
When consumed in controlled amounts as part of a balanced diet, palm oil can be a healthy option for humans. It offers several health advantages over other vegetable oils due to its unique composition and potential health benefits.
Including palm oil into your diet might enhance the absorption of essential vitamin A, which is crucial for maintaining healthy retinas and overall eye function. Vitamin A falls under the category of fat-soluble vitamins, meaning that you need dietary fat to ensure efficient absorption. Including palm oil in your meals has demonstrated the capacity to increase your body’s capability to absorb vitamin A effectively, potentially extending to other fat-soluble vitamins as well.
Lower Saturated Fat Content:
One notable advantage of palm oil is its relatively low saturated fat content compared to some other vegetable oils. While saturated fats are necessary in moderation, excessive consumption can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The difference between palm oil and other vegetable oils is that palm oil contains a specific type of saturated fat called palmitic acid. Unlike trans fats or most other saturated fats that have been associated with raising LDL cholesterol levels, palmitic acid in palm oil has a neutral impact on blood cholesterol levels.
Compared to some other vegetable oils, palm oil contains a balanced composition of both saturated and unsaturated fats and is a rich source of tocotrienols and tocopherols, which are forms of vitamin E with antioxidant properties. These compounds help reduce oxidative stress and promotes cardiovascular health.
By incorporating palm oil as a cooking ingredient, individuals can make a conscious choice to promote heart health and reduce the potential risks associated with excessive saturated fat consumption.
It’s important to note that while palm oil offers these advantages, there are also significant environmental and ethical considerations associated with its production, including deforestation and habitat destruction. As a consumer, it’s wise to make informed choices and support sustainable sourcing practices when selecting products that contain palm oil.
Rich in Antioxidants:
Palm oil is a rich source of antioxidants, which play a vital role in protecting our bodies against free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage cells. The presence of antioxidants in palm oil, particularly carotenoids such as beta-carotene and lycopene, can help combat the harmful effects of these free radicals.
A particular form of vitamin E found in palm oil, known as tocotrienol, has demonstrated a superior ability to safeguard brain tissue from harmful free radicals when compared to other antioxidants. A study cited by WebMD revealed that tocotrienols from palm oil might even have the potential to halt the progression of brain lesions.
It could also contribute to improved heart health. The antioxidative properties of vitamin E in palm oil appear to have a positive impact on the advancement of heart disease in certain patients, potentially reducing its progression or even stopping it. Although further research is necessary to replicate these findings, palm oil extract holds promise as a potential aid for individuals combating heart disease.
Nutrient-Rich Profile:
Palm oil offers a range of essential nutrients that support overall health. It contains tocotrienols, a type of vitamin E that exhibits potent antioxidant properties. Additionally, palm oil contains vitamin K, which is crucial for blood clotting and bone health. These nutrients contribute to the overall nutritional value of palm oil and make it a beneficial addition to a balanced diet.

Stability at High Temperatures:
When it comes to cooking oils, stability under high temperatures is a significant consideration. Palm oil has a high smoke point, which means it can withstand high heat without breaking down or oxidizing. This stability makes palm oil suitable for frying and sautéing without the risk of producing harmful compounds.
Shelf Life and Texture:
The natural composition of palm oil contributes to its extended shelf life compared to other vegetable oils. The presence of saturated fats in palm oil helps prevent rancidity, resulting in a longer-lasting product. Moreover, the semi-solid texture of palm oil at room temperature makes it a preferred choice for certain culinary applications, such as in baking and pastry making [2].
While palm oil has faced some criticism due to concerns about deforestation and its impact on the environment, it is important to assess its health benefits objectively. When consumed in moderation and sourced responsibly, palm oil can be a part of a healthy diet. Its lower saturated fat content, rich antioxidant profile, nutrient content, stability at high temperatures, and longer shelf life make it a viable alternative to other vegetable oils.
As with any dietary choice, it is essential to consider individual health conditions and consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist. Ultimately, making informed decisions and maintaining a varied and balanced diet remains crucial for optimal health and well-being.